Evaluation Driven AI Development
evaluationEvaluation Driven AI Development is a recommended development practice for building and improving robust AI applications, emphasizing continuous evaluations and testing throughout the development lifecycle.
These evaluations—or “evals”—act as end-to-end tests for AI behavior. They measure output quality across defined dimensions such as relevance, correctness, helpfulness, or even fairness, using automated assertions and LLM judgments.
For us it is the Test-driven-development equivalent for AI systems.
Motivation
Developing AI applications often involves trade-offs: improving quality for one question or use case can degrade results for others. Unlike traditional software, binary pass/fail testing is rarely possible. Instead, continuous benchmarking, trend analysis, and integration of real user feedback are required to evaluate and improve AI system quality.
Evaluation-Driven Development makes repeatable LLM evaluations the core step of the development lifecycle. Instead of heuristically “tuning” prompts, models, or retrieval, changes are accepted only when they improve metrics and benchmarks. This reduces regression risk, makes changes explainable, and enables CI/CD gates for agents, RAG pipelines, and chat flows.
Teams can monitor trends across runs (not single snapshots) and can reliably block regressing PRs.
Teams building AI products should treat evals as first-class development artifacts. Maintain them in version control, run them in CI/CD pipelines, and iterate against them as you would unit or integration tests in conventional systems. Evaluation Driven AI Development doesn’t eliminate subjectivity—it manages it.
A new "AI-Native" development cycle
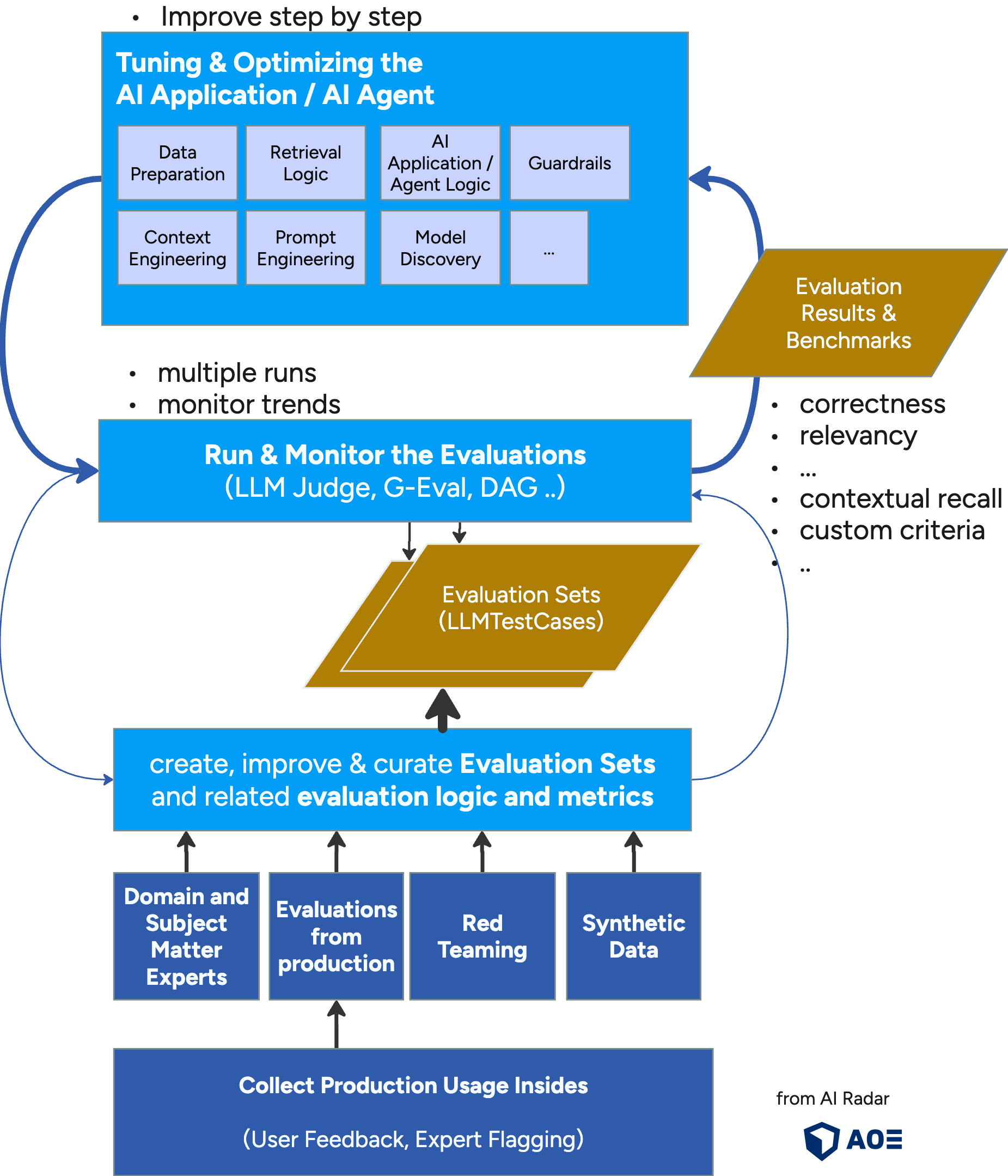
As the image shows - the evaluation driven development cycles contain the following main steps:
curate evaluation sets & related evaluation logic and metrics: Create evaluation sets with LLM test case. Different sets can be used for different aspects (e.g. golden set, hard negatives, online evals). Version and freeze dataset states. * Use "Red Teaming" to test "bad" cases. * Collect real-world evaluations based on user feedback and usage monitoring * Use experts / human feedback to define cases
Run & monitor: Execute evaluations during development and automatically in CI/CD. Run multiple times for non deterministic evaluations. Track trends.
Tune deliberately: During tuning change only one aspect at a time and measure impact. The process of tuning can be a complex one and typically include the following aspects:
- Tune your system prompt. See Prompt Engineering
- Tune the retrival of knowlegde or even update the retrieval architecture. See related articles Advanced & Modular RAG, Graph RAG and Smart Vector Database Usage
- Tune the preparation and indexing of your data (e.g. extraction, chunking strategies, embeddings)
- Try out different models. See article Model Discovery & Selection
- Optimize Tool Usage
- Optimize Guardrails
- Optimize the whole context (see Context Engineering)
Gates & regression protection:
- Releases proceed only if benchmarks are held or improved.
- Also use evaluations to test your guardrails. See Prompt Injection Awareness
What could be measured?
Output quality:
- Correctness: Final answer matches ground truth or required logic.
- Relevance (to the question): The answer addresses the user intent (on-topic).
- Completeness: Required aspects are present.
- Consistency: No internal contradictions across turns/sections.
Retrieval quality (RAG):
- Contextual Recall: does the context cover the facts needed for the “ideal answer”?
- Context Precision: Fraction of retrieved context actually used by the answer.
- Answer Relevancy: is the answer supported by the retrieved context?
- Groundedness/Hallucination: are citations/evidence present?
Task-/domain-specific:
- Format/structure compliance (e.g., JSON/Markdown schema)
- Correct tool calls (parameters, order, error handling)
- domain specific complex criteria metrics (e.g. using DAG or custom Evaluation Prompts)
Guardrails
- Safety/policy criteria (PII leaks, jailbreak resistance)