graph RAG
retrievalGraph RAG (Graph-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation) or GRAG (Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is a powerful AI-based content interpretation and retrieval mechanism that combines retrieval-augmented generation with knowledge graphs (graph databases). Instead of relying solely on unstructured document retrieval, Graph RAG leverages structured relationships between entities, enabling more precise and context-aware information retrieval for LLM-based agents.
There are different graphRAG patterns and techniques, and we consider Graph RAG techniques as a more advanced approach that can be used for more complex and enterprise use cases.
In this article we give an overview of the different aspects of graphRAG techniques.
What is a Knowledge Graph (=KG)?
A knowledge graph is a structured representation of entities (such as people, places, or concepts) and their relationships, typically modeled as nodes and edges in a graph database. Knowledge graphs enable machines to reason about data by capturing explicit semantics and connections, supporting advanced retrieval. They are widely used in search, recommendation, and question answering systems.
How it works in general
- Graph Construction / Indexing: Data is ingested into a graph structure (e.g., using Neo4j, TigerGraph, NebulaGraph or open-source libraries). Domain specific graphs may already exist and can be of great value for the application. Or you can build your own graph from data and documents during indexing.
- Retrieval: At query time, relevant nodes and their relationships are retrieved based on the user's intent, often using graph traversal or embedding-based similarity.
- Augmentation: Retrieved graph substructures are provided as context to the LLM, improving factuality, reasoning, and multi-hop question answering.
Typical Use Cases
- Enterprise knowledge management
- When relationships between entities are critical for retrieval or reasoning.
- Scientific literature search
- Multi-hop QA and reasoning
KG and LLMs
We are focusiing on the two ways how LLM and KG interact:
- LLMs as tool to build/extract KG (indexing)
- KGs as input/context into LLM (retrieval & augmentation)
Indexing and Graph Construction
Graph structures can originate from various sources, from a structured business domain, (hierarchical) document representations, and signals computed by graph algorithms.
For GraphRAG to work, data must be structured as a meaningful graph. This involves modeling key nodes and relationships, then building or importing the graph accordingly.
A knowledge graph for GenAI typically involve two types:
Domain graph – models real-world concepts relevant to your app. NER (Named Entity Recognition) can be used to extract entities and relations from text.
Lexical graph – represents document structure (text chunks, sections, etc.).
Both are often combined for richer context.
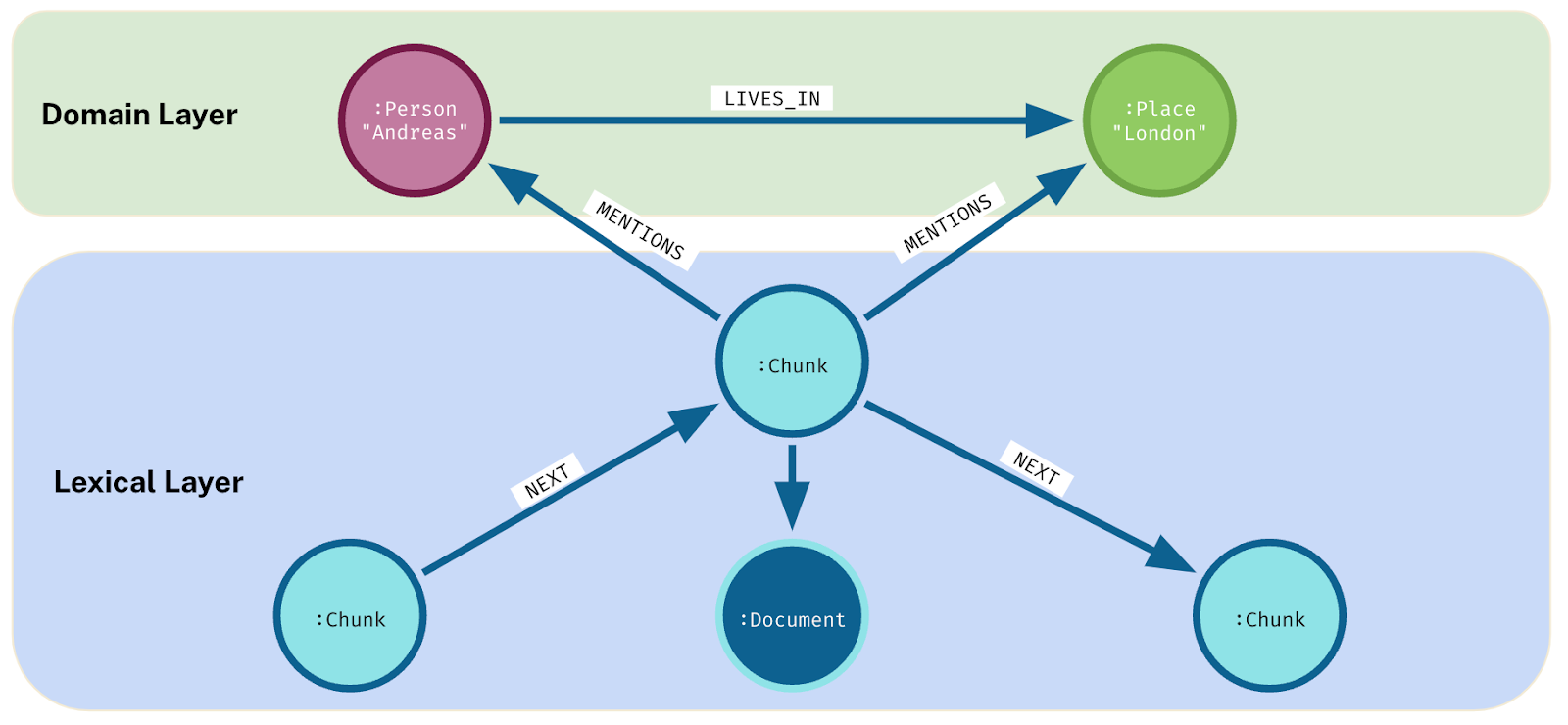
Graph Retrieval
Graphs can be navigated (traversed) by following simple patterns like (node:Type)-[relationship:TYPE]->(node:Type) or by using Cypher or GQL.
GraphRAG retrieves data by starting from search results (vector, text, spatial, etc.) and then follows related nodes to gather more relevant info. It considers user context and filters/ranks the data before using it to enhance the response.
Typical approaches:
- Use vector similarity search (embeddings) and use case specific path traversal (e.g. to find the parent chapter..)
- Use (Cyper) Query Templates that are filled (use case specific queries)
- Use Text2Cypher Tools
Notable resources
- GraphRAG Pattern
- Neo4j GraphRAG Field Guide - List of graph retrieval patterns
- Neo4j What is graphRAG
- LlamaIndex Property Graph Index
- graphRAG Paper by Microsoft Research
- graphRAG Implementation by Microsoft
- nano-graphrag (GitHub)