How to use the AI Technology Radar
The Radar around the Development of professional AI Agents, RAG Systems and LLMOps.
Introduction
Everyone’s talking about agents. Few are building systems that actually work in production. This Radar is a guide to help you navigate the complex landscape of AI and RAG development.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), especially agentic AI systems and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), is evolving at a rapid pace. New frameworks, methods, models, and tools continuously emerge, making it challenging yet essential to remain informed.
As a team involved in AI application development and implementation, it is crucial to actively explore and evaluate new innovations and regularly reassess existing technologies to ensure we always leverage the most suitable solutions for our needs. However, it remains important to wisely select technologies that effectively align with our projects and requirements. There is no one-size-fits-all solution.
RAG and AI Agent Basics
New to AI Agents and RAG? We have a short summary for you:
RAG
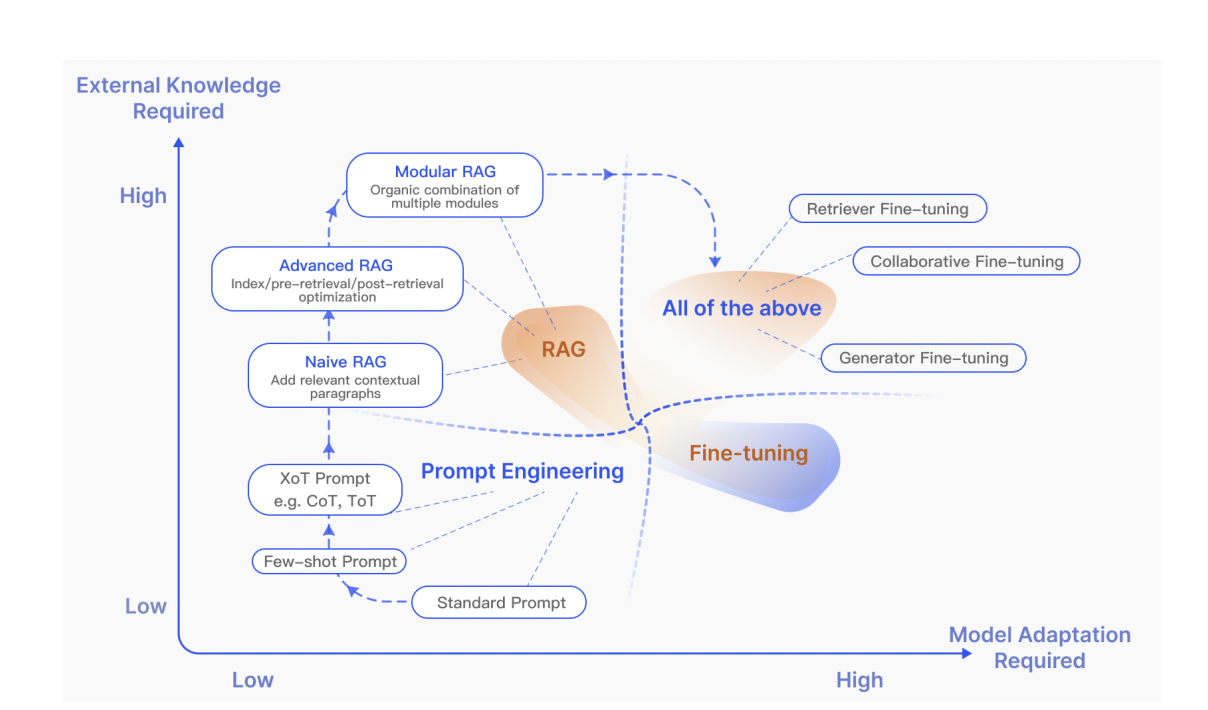
RAG ("Retrieval-Augmented Generation") is a technique that enhances Large Language Model (LLM) responses by retrieving source information from external data stores to augment generated responses. This technique is often used to work with use case specific content and knowledge. The term is used in different combination with certain prefixes to describe the type or paradigms of RAG system or RAG architecture (e.g. "GraphRAG", "SelfRAG", "Agentic RAG", ...).
A high level overview for RAG Paradigms:
- naive RAG: Simple retrieval > augmentation > generation steps.
- advanced RAG: Pre-retrieval (query rewriting, query expansion..)> retrieval > post-retrieval (e.g. rerank) > generation steps.
- modular RAG: contains more complex patterns, which require orchestration and routing of the user query.
Agents
Also for AI Agents there are many different definitions. Here are some common ones:
- "Agentic AI uses sophisticated reasoning and iterative planning to autonomously solve complex, multi-step problems" (Nvidia)
- "Agentic AI is characterised by its ability to act on behalf of an organisation, making decisions based on data analysis and predefined goals." (Gartner)
The term "agent" is around for a while - but nowadays one often refers to advanced AI Agents, that use the possibilties of SOTA Models (LLM) and have access to data and tools to (autonomously) perform its tasks. The following graphic illustrates this:
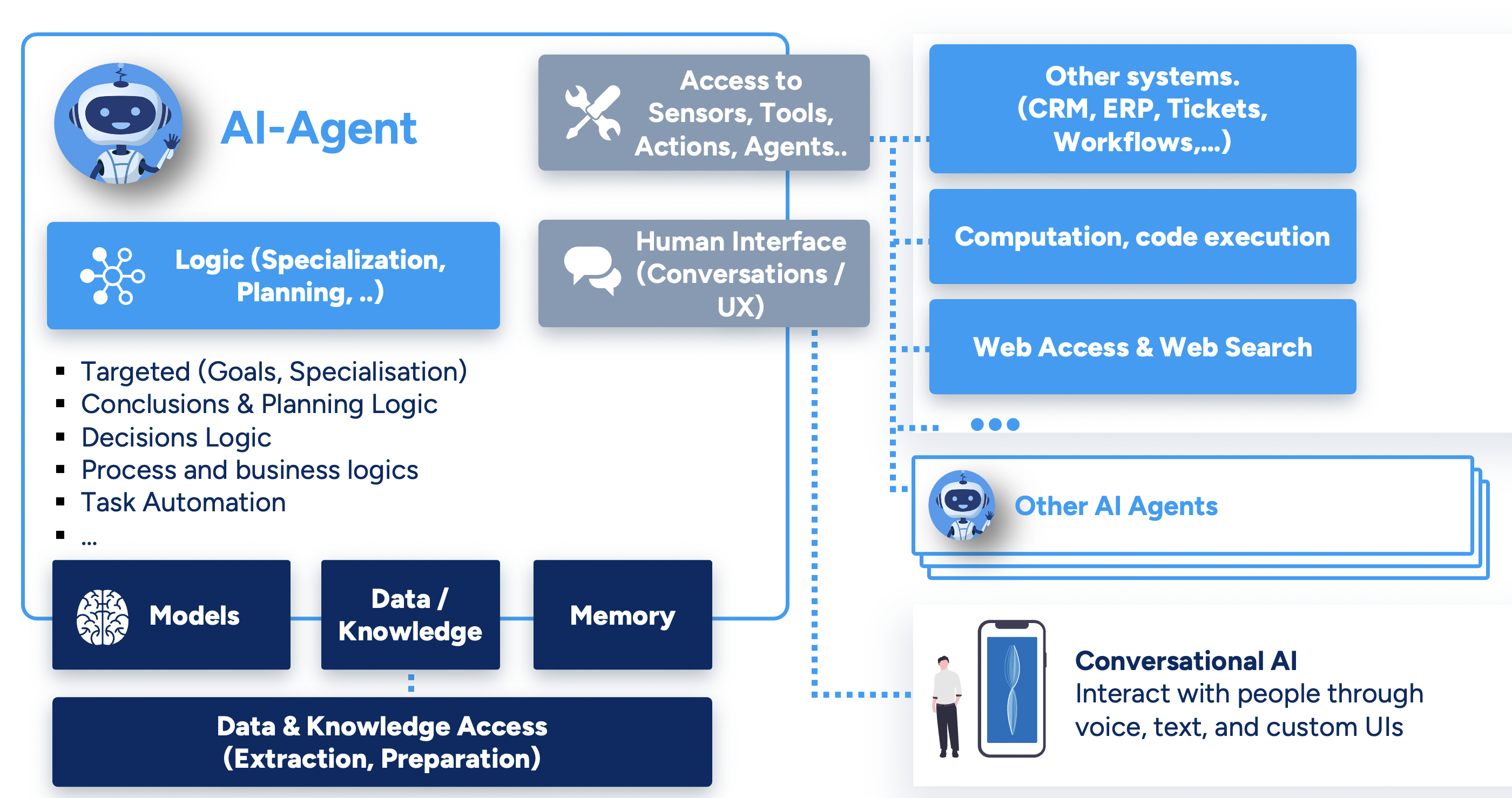
Essentially AI Agents are applications that use the capabilities of LLMs to autonomously perform tasks. That allows a completly new way to build systems: Using "higher intelligence", human like "communication" and nuanced reasoning. Agents can therefore handle complex tasks, make decisions, and manage workflows without constant human input. Agentic systems often consits of the following elements:
- Model: One or more LLMs, that are used for reasoning and decision making. See Model Discovery
- Tools: External tools that the agent can use to perform tasks. Tools can be further differenciated:
- Data Access: Access to data & informations used to build context
- Action: Interact with systems. Available Tools are often given in the LLM context, so that the reasoning process can "decide" to use them.
- Orchestration: Other agents are made available. See Multi Agent Systems.
- Instructions and Logic: Guidelines, Instructions, Businesslogic, Guardrails etc. Instructions should be clear and optimizing them is an important practice. See Prompt Engineering.
Modular RAG systems and AI agents are overlapping - and use similar patterns and frameworks. For professional AI applications aspects like: retrieval techniques, augmentation, prompting, tool usage, strategies, archiecture patterns and the continuous evaluation and observation of these applications are highly relevant. And this is what the radar is about:
What is the AI & RAG Technology Radar?
This radar provides an overview of key technologies, frameworks, patterns, tools, and platforms specifically relevant for developing AI agents and RAG applications. We highlight technologies that we consider noteworthy or emerging, as well as significant updates or shifts in the landscape. Previously listed items remain accessible in the comprehensive overview and via search functionality.
What it is not
This is not a comprehensive directory of all available tools, models, or AI startups. Instead, the Techradar selectively highlights key entries that are particularly relevant to engineering practices. Where appropriate, we include curated links to related overviews and external resources (that you should have on the radar). For example:
- Tool-Finder — A curated list to discover AI tools and products.
- Model Benchmarks & Leaderboards — An overview of key benchmarking platforms and leaderboards to track model performance across tasks.
How it is created
Technologies included in the radar are recommended by teams actively working with AI and RAG implementations. Every item listed has been evaluated or implemented in real-world scenarios.
Discussions across expert teams ensure thorough consideration and accurate descriptions and categorization. The result should be a comprehensive, reliable reflection of the current AI and RAG technology landscape.
How should it be used
This radar serves as a guide to ensure that teams are well-informed about key technologies shaping AI and RAG systems.
The goal is to inspire and guide the teams’ daily work and support informed, strategic decision-making. Additionally, the radar aims to provide insights and context, allowing a deeper understanding of each technology.
We also hope the radar proves valuable and inspiring to the broader AI development community.
We categorize items into six distinct segments to structure the broad range of technologies involved in AI Agent development:
The segments are:
Pattern & Architectures: Covers architectural patterns, strategies and standards essential for designing, building, and integrating robust AI agents and systems.
Frameworks: Includes frameworks specifically targeted for AI application development, facilitating efficient implementation and scalability.
Models & Platforms: Highlights AI models selection, usage, and platforms that offer deployment and hosting capabilities for models.
Evaluation & Observability: Addresses tools and platforms dedicated to evaluating, testing, monitoring, and optimizing AI systems, including frameworks for effective model lifecycle management.
Data, Feature Extraction & Storage: Focuses on methods and tools related to data collection, preparation, feature extraction, and their management and storage.
Other Tools: Lists various tools and utilities that are overarching or cross-cutting, including low-code platforms and general AI workflow management tools.
Each of the items is classified in one of these rings:
Adopt: Strongly recommended technologies proven in production environments, demonstrating stability, performance, and clear benefits.
Trial: Technologies that have shown positive initial results and are recommended for further exploration and evaluation in pilot projects.
Assess: Promising technologies that warrant deeper examination, suitable for experimentation when specific project needs arise.
Hold: Technologies we advise against adopting or continuing to use. They may still be acceptable in legacy systems, but superior alternatives have emerged, and transitioning away is recommended.
Contributing to the AI & RAG Technology Radar
The AI & RAG Technology Radar welcomes contributions and collaboration from the community. You can find the radar source code and contribute directly on GitHub: